Introduction
A careful assessment from the situations surrounding a conveyor is important for exact conveyor chain choice. This segment discusses the basic considerations essential for prosperous conveyor chain variety. Roller Chains are often used for light to moderate duty materials handling applications. Environmental ailments may perhaps require the usage of distinctive products, platings coatings, lubricants or the ability to operate without supplemental external lubrication.
Simple Information and facts Essential For Chain Choice
? Type of chain conveyor (unit or bulk) including the process of conveyance (attachments, buckets, via rods etc).
? Conveyor layout together with sprocket places, inclines (if any) as well as the number of chain strands (N) to be made use of.
? Amount of materials (M in lbs/ft or kN/m) and sort of materials to get conveyed.
? Estimated excess weight of conveyor parts (W in lbs/ft or kN/m) such as chain, slats or attachments (if any).
? Linear chain velocity (S in ft/min or m/min).
? Environment in which the chain will operate such as temperature, corrosion circumstance, lubrication condition etc.
Phase 1: Estimate Chain Tension
Utilize the formula beneath to estimate the conveyor Pull (Pest) after which the chain stress (Check). Pest = (M + W) x f x SF and
Check = Pest / N
f = Coefficient of Friction
SF = Speed Factor
Stage two: Produce a Tentative Chain Selection
Applying the Test worth, create a tentative choice by picking out a chain
whose rated working load better than the calculated Test value.These values are suitable for conveyor services and are diff erent from people shown in tables on the front from the catalog that are related to slow speed drive chain usage.
Additionally to suffi cient load carrying capability frequently these chains needs to be of the specific pitch to accommodate a desired attachment spacing. By way of example if slats are to become bolted to an attachment each one.five inches, the pitch in the chain chosen must divide into one.5?¡À. Hence one particular could use a 40 chain (1/2?¡À pitch) using the attachments every 3rd, a 60 chain (3/4?¡À pitch) using the attachments every 2nd, a 120 chain (1-1/2?¡À pitch) with the attachments every single pitch or even a C2060H chain (1-1/2?¡À pitch) using the attachments each pitch.
Stage three: Finalize Assortment – Calculate Real Conveyor Pull
Just after building a tentative selection we need to verify it by calculating
the real chain stress (T). To do this we should fi rst calculate the real conveyor pull (P). From the layouts shown to the correct side of this page pick out the proper formula and determine the complete conveyor pull. Note that some conveyors could possibly be a blend of horizontal, inclined and vertical . . . in that case calculate the conveyor Pull at each and every section and add them together.
Stage four: Determine Highest Chain Tension
The maximum Chain Tension (T) equals the Conveyor Pull (P) as calculated in Phase three divided from the amount of strands carrying the load (N), occasions the Pace Component (SF) shown in Table 2, the Multi-Strand Issue (MSF) shown in Table 3 plus the Temperature Factor (TF) shown in Table four.
T = (P / N) x MSF x SF x TF
Step five: Verify the ?¡ãRated Operating Load?¡À of your Chosen Chain
The ?¡ãRated Functioning Load?¡À on the picked chain should really be greater compared to the Maximum Chain Tension (T) calculated in Phase 4 over. These values are ideal for conveyor service and therefore are diff erent from those proven in tables on the front of the catalog which are linked to slow speed drive chain usage.
Stage 6: Check out the ?¡ãAllowable Roller Load?¡À of your Picked Chain
For chains that roll over the chain rollers or on top roller attachments it really is needed to check out the Allowable Roller Load?¡À.
Note: the Roller load is determined by: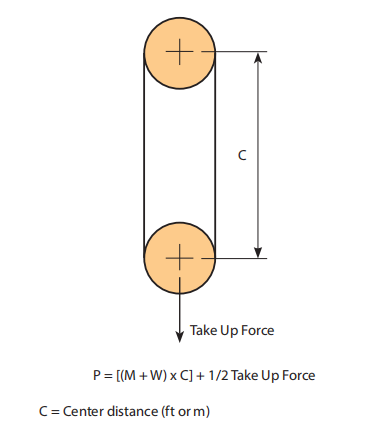 Roller Load = Wr / Nr
Roller Load = Wr / Nr
Wr = The complete bodyweight carried through the rollers
Nr = The quantity of rollers supporting the weight.